Detailed Test Information


The GI360 is a comprehensive multi-technology stool test specifically developed to provide clinically actionable results, including standardised dysbiosis index and live susceptibility testing, this breakthrough test utilises the widest array of highly validated technologies in one test.
The GI360™ Profile utilises new evidence-based DNA mapping technology coupled with growth-based culture and ID by MALDI-TOF, sensitive biochemical assays and microscopy. The ultimate combination to detect and assess the status of pathogens, viruses, parasites and bacteria that may be contributing to acute or chronic gastrointestinal symptoms and disease.
With such a comprehensive overview of patients GI health, the GI360 provides practitioners with valuable information for uniquely tailored treatment strategies.

Why is it important?
It is important to continue testing culture alongside using DNA methods. Culture is considered the gold standard for stool microbiology, and is the only method that allows isolating organisms for standardised antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and facilitates advanced MALDI-TOF species identification.
Traditionally in Microbiology there are 3 different growth conditions considered. Doctors Data looks at 10 different growth conditions.
When there are deficiencies in expected bacteria, mucosal barriers are compromised, which can result in:

MALDI-TOF is utilised to identify specific pathogenic and dysbiotic species. At Doctor’s Data they ensure accurate results through regular equipment calibrations and highly skilled technicians.
This microbiology testing is able to identify more than 1400 organisms, including imbalanced and pathogenic bacteria. MALDI-TOF technology is “open database”, so it can identify unlimited new organisms.
What is it?
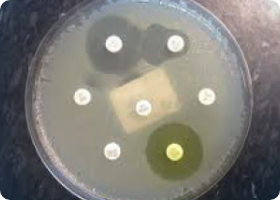
Ensures targeted & effective treatment
Using the pathogens detected by MALDI-TOF, EVERY single patient’s sample is tested using the diffusion method to identify the zones of inhibition which are unique to each patient – evaluating phenotypic expression, for reliable eradication strategies (including yeasts). Doctor’s Data includes both pharmaceutical agents as well as botanicals in their susceptibility testing.
Doctors Data simplify the report by marking the colony forming units (CFU’s) as
1+ to 4+ for MALDI-TOF results. (These indicate the scientific notation range):
1+ = <103 | 2+ = 103-104 | 3+ = 105-106 | 4+ = >107
DNA results are represented in standard deviations (-3 to +3)
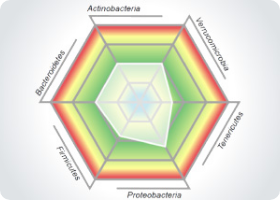
What is it?
This data is collected by Multiplex PCR 16sRNA
The technology has a higher specificity to capture a varied range of organisms in the patient’s stool and can get down to the specific sub-species compared to other PCR methods which are less specific. This allows for more accurate and reproducible identification of what is actually in the patients sample. The technology used has several research papers in supporting it’s validity behind identification of particular species for IBS & IBD. This is Multiplex PCR testing, measuring Microbiome bacterial abundance and diversity, through DNA analysis of 45+ organisms.

Why is it important to test?
Yeast are not uniformly dispersed throughout the stool and this may lead to undetectable or low levels of yeast identified by microscopy, despite culture and identified yeast species. Conversely, microscopic examination may reveal a significant amount of yeast present but no viable yeast cultured. Yeast may not always survive through the intestines. Nonviable diet-derived yeast may also be detected microscopically.
Why is it important to test?
SCFAs are the end product of the bacterial fermentation process of dietary fibre by beneficial flora in the gut and play an important role in the health of the GI as well as protecting against intestinal dysbiosis. Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria produce large amounts of SCFAs, which decrease the pH of the intestines and therefore make the environment unsuitable for pathogens, including bacteria and yeast. Studies have shown that SCFAs have numerous implications in maintaining gut physiology. SCFAs decrease inflammation, stimulate healing, and contribute to normal cell metabolism and differentiation. Levels of Butyrate and Total SCFA in mg/mL are important for assessing overall SCFA production, and are reflective of beneficial flora levels and/or adequate fibre intake.
Butyrate is a major regulator of mucosal barrier integrity and mediates the release of anti inflammatory cytokines by epithelial cells. It is fuel for enterocytes, and it also mediates microbial cross talk.
Why is it important to test?
Inflammation can significantly increase intestinal permeability and compromise assimilation of nutrients. The extent of inflammation, whether caused by pathogens or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can be assessed and monitored by examination of the levels of biomarkers such as lysozyme, lactoferrin, white blood cells and mucus via this stool test.
These markers can be used to differentiate between inflammation associated with potentially life-threatening inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which requires lifelong treatment, and less severe inflammation that can be associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) which is frequently due to the presence of enteroinvasive pathogens. Lactoferrin is only markedly elevated prior to and during the active phases of IBD, but not with IBS. Monitoring faecal lactoferrin levels in patients with IBD can therefore facilitate timely treatment of IBD, and the test can be ordered separately.
Why is it important to test?
IgA is secreted by mucosal tissue and represents the first line of defense of the GI mucosa and is central to the normal function of the GI tract as an immune barrier. Elevated levels of sIgA have been associated with an upregulated immune response.
If there is elevated sIgA levels when there is dysbiosis or a parasite present, this indicates that there is a normal immune response.
If there is low sIgA when there is dysbiosis or a parasite present, it may indicate a lowered immune response – therefore improving gut immunity should be prioritised.
Elastase
Elastase findings can be used for the exclusion of pancreatic insufficiency. Correlations between low levels and chronic pancreatitis and cancer have been reported. Decreased Elastase may also be seen in alcoholism or a past history of alcoholism.
Fat Stain
Microscopic determination of faecal fat using Sudan IV staining is a qualitative procedure utilised to assess fat absorption and to detect steatorrhea.
Muscle Fibres
Muscle fibres in the stool are an indicator of incomplete digestion. Bloating, flatulence, feelings of “fullness” may be associated with increase in muscle fibers.
Vegetable fibres in the stool may be indicative of inadequate chewing, or eating “on the run”.
Carbohydrates
The presence of reducing substances in stool specimens can indicate carbohydrate malabsorption.
What is it?
Beta-glucuronidase is an enzyme that breaks the tight bond between glucuronic acid and toxins in the intestines. The binding of toxins in the gut is protective by way of blocking their absorption and facilitating excretion. Higher levels of beta-glucuronidase may be associated with an imbalanced intestinal microbiota profile, as well as higher circulating oestrogens and lower faecal excretion of oestrogens.

What does it provide?
GI360 utilises multiplex DNA technology, testing for multiple pathogens and parasites (for which genetic probes exist for), to assist with identification.

What is it?
Registering is easy and obligation-free!
Gain access to trusted product and functional testing brands, cutting-edge research and education.
Plus, gain an ongoing 20% discount on all self testing, as well as a 20% off introductory offer on products.
If you are based in New Zealand you can access GI360 testing via FxMed.

In this 30 minute webinar, Joel E. Mortensen, PhD, covers questions from the field regarding new technologies in microbiome testing and the research behind the GI360 test.
GI360 Complete:
$599.00
GI360 Select
$499.00
GI360 Essentials:
$455.00
GI360 Microbiome:
$269.00

Doctor’s Data, Inc. has provided innovative speciality testing to healthcare practitioners around the world from our advanced, CLIA-licensed clinical laboratory since 1972.
A specialist and pioneer in essential and toxic elemental testing, the laboratory provides a wide array of functional testing to aid in decision-making and better patient outcomes. Choose DDI to help you assess and treat heavy metal burden, nutritional deficiencies, gastrointestinal function, cardiovascular risk, liver and metabolic abnormalities, and more.

Registering is easy and obligation-free!
Gain access to trusted product and functional testing brands, cutting-edge research and education.
Plus, gain an ongoing 20% discount on all self testing, as well as a 20% off introductory offer on products.
If you are based in New Zealand you can access GI360 testing via FxMed.

Jess is a qualified Nutritionist with a Bachelor of Health Science in Nutritional Medicine. She believes that there is no one size fits all approach and is passionate about educating, inspiring and supporting clients and practitioners with a customised approach to healthcare. Specialties include preconception, pregnancy, post-natal and infant care.
Jess is excited to build relationships, educate and share her knowledge with both retail and practitioners in South Queensland and Northern NSW.

Lauren is an NHAA accredited Clinical Naturopath with a Bachelor of Health Science. She is incredibly passionate about natural health and educating clients on the foundational importance of nutrition, lifestyle and stress management and believes complimenting these building blocks with nutraceutical support and functional testing often holds the key to optimal health and vitality. Lauren looks forward to supporting practitioners and clients in these key areas.
Specialties include supporting thyroid health, digestive disorders and mental health.